CONNECT
When you hear the word robotics, what images or ideas come to your mind? For you, what are robots?
Robotics is the science that uses technology to develop and build robots. These machines are made to perform tasks independently or controlled through commands, with the aim of facilitating and assisting human activities.
In educational robotics classes we research, make discoveries and build prototypes. They can be animal constructions, toys, tools or even machines that imitate what exists in real life.
With technological structural assembly kits, made up of many colorful parts, we have at hand an investigative tool to explore the simplest concepts of structural construction.
To start structural robotics classes, you need to understand some basic technological concepts, such as bases, beams, connectors, wheels and levers.
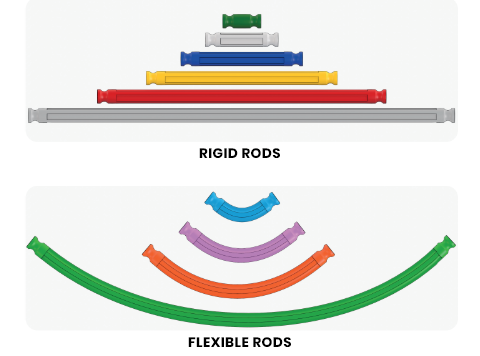
The bases and beams are fundamental pieces to start assembling a project. They are responsible for supporting and structuring the other components. Just like the bases, the beams are part of the project structure. In the structural robotics kit, beams are called rods and come in two types: rigid and flexible.
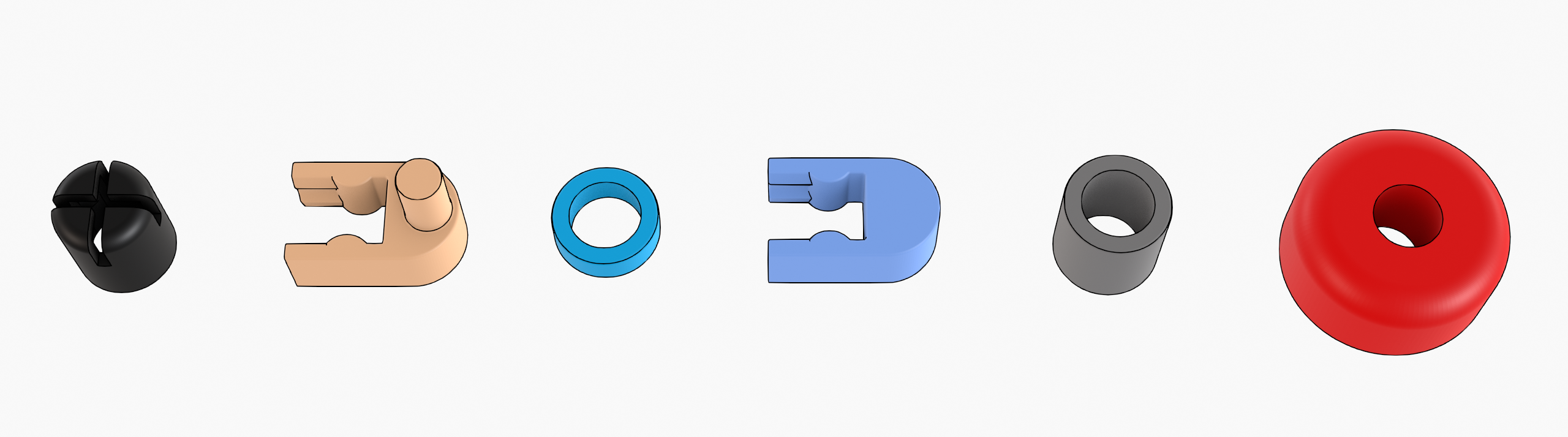
Connectors are parts used to connect components (connect parts) of the project. Connectors can be parts that fit into others by pressure and can have different sizes, shapes and colors.
 Wheels are circular objects that facilitate the transport of loads. Axles are objects with a cylindrical shape, smaller than the wheels, which are used to join them. In the structural robotics kit, the axes are called rods.
Wheels are circular objects that facilitate the transport of loads. Axles are objects with a cylindrical shape, smaller than the wheels, which are used to join them. In the structural robotics kit, the axes are called rods.
The wheels and axles always rotate at the same speed. Moving a vehicle or heavy object using wheels makes the process easier.
Auxiliary parts are responsible for performing functions such as finishing, spacing and interconnection between parts.
CONTEMPLATE
Look at your team’s structural robotics kits:
• What are the auxiliary parts for?
• What are the axles of a wheel?
CONSTRUCT
Levers are tools that help us move heavy objects. They are long bars that rotate around a support point. With levers we can apply a smaller force to lift or push very heavy objects. They are found in toys such as seesaws and in large machines and buildings. Levers are special tools, as they make our work easier and help us do incredible things!
Now, to use the lever you need to know two important pieces of information:
• The right point to hold the lever. Imagine you want to lift a heavy object. If you hold the lever close to the object, it will be easier to lift it, but you will have to make more effort.
If you hold the lever at a point further away from the object, it will take less effort, although it will be more difficult to lift it.
• The power of distance. To lift a heavy object with the lever, it is necessary to apply a smaller force over a greater distance from the lever. It’s as if you gave the lever a “little push” for it to do the rest of the work.
Levers are classified as:
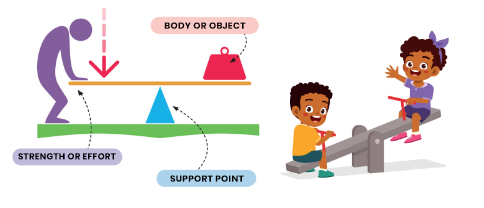
• Interfixed: is one in which the support point is between the force and the load. Example: seesaw. In it, we can lift the body or object at the other end with just the weight of our own body.

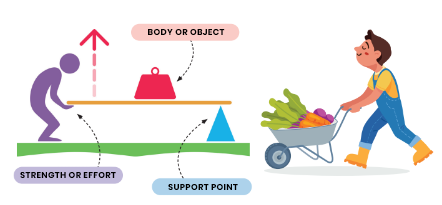
• Inter-resistant: this is when the load is between the support point and the force. Example: wheelbarrow. In it, the support point is the front wheel, which helps us transport something heavy effortlessly.
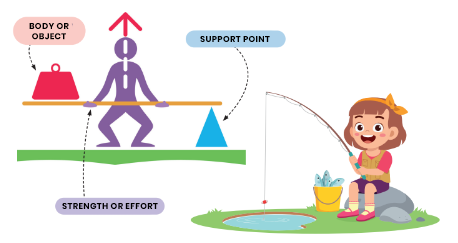
• Interpotent: is when the force is between the load and the support point. Example: fishing rod. To catch a big fish, you need to hold the fishing rod with a little force and wrap the line around the hook.

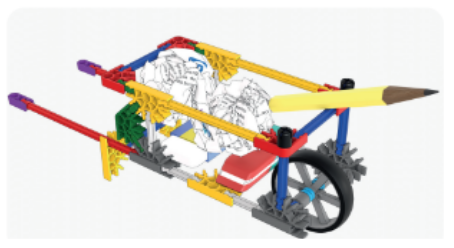
Now, choose two of the suggested prototypes and assemble them using the parts from the structural robotics technology kit. Follow the step by step and, at the end, observe the differences between the constructions.
CONTINUE
After building the prototypes, share your experiences with your team and respond:
• Did you notice the difference between the assembled levers?
• Which lever was most difficult to build?
Then put away all the materials.